Home
| About
| Mine Tracker
| RSS
| Footer
▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄▄ █▄▄░▄▄█░▄▄▀█░▄▄▀█▀▄▀█░▄▄███░▄▄▀█░▄▄▀█░▄▀███▄▄░▄▄█░▄▄▀█░▄▄▀█▀▄▀█░▄▄█░▄▄▀█░▄▄▀██▄██░███▄██▄░▄█░██░ ███░███░▀▀▄█░▀▀░█░█▀█░▄▄███░▀▀░█░██░█░█░█████░███░▀▀▄█░▀▀░█░█▀█░▄▄█░▀▀░█░▄▄▀██░▄█░███░▄██░██░▀▀░ ███░███▄█▄▄█▄██▄██▄██▄▄▄███▄██▄█▄██▄█▄▄██████░███▄█▄▄█▄██▄██▄██▄▄▄█▄██▄█▄▄▄▄█▄▄▄█▄▄█▄▄▄██▄██▀▀▀▄ ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀
Preferred by Nature
https://www.preferredbynature.org/
Preferred by Nature is a non-profit organisation that supports better land management and business practices that benefit people, nature and climate.
https://www.preferredbynature.org/
Preferred by Nature is a non-profit organisation that supports better land management and business practices that benefit people, nature and climate.
The International Sustainability and Carbon Certification (ISCC)
https://www.iscc-system.org/
The International Sustainability and Carbon Certification (ISCC) is an independent multi-stakeholder initiative and leading certification system supporting sustainable, fully traceable, deforestation-free and climate-friendly supply chains. With our certification we contribute to environmentally, socially and economically sustainable production.
https://www.iscc-system.org/
The International Sustainability and Carbon Certification (ISCC) is an independent multi-stakeholder initiative and leading certification system supporting sustainable, fully traceable, deforestation-free and climate-friendly supply chains. With our certification we contribute to environmentally, socially and economically sustainable production.
GS1 Digital Link Standard: URI Syntax
https://www.gs1.org/docs/Digital-Link/GS1_Digital_Link_Standard_URI_Syntax_r_i1-2-1_2022-02-08.pdf
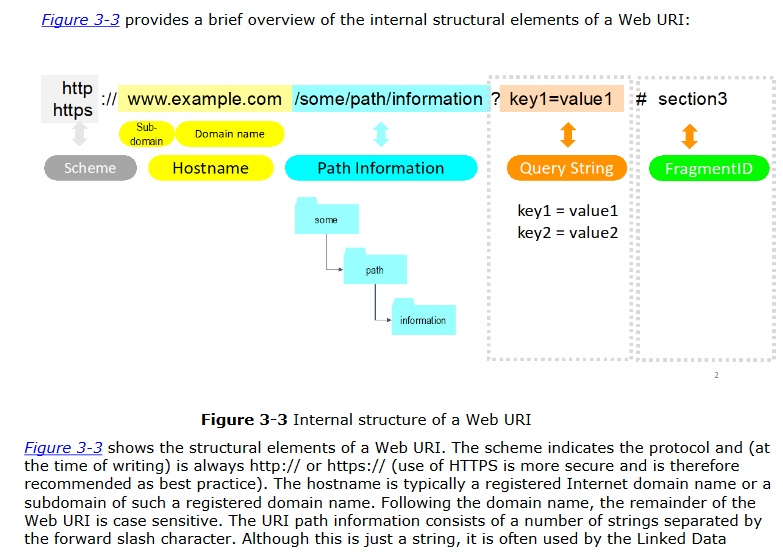
This document provides some of the background to the design of GS1 Digital Link, highlighting existing techniques and practices that underpin the World Wide Web, and applying those to the GS1 system. The normative portions set out the detailed syntax of Web addresses (HTTP URIs) that encode GS1 identifiers with exactly the same precision and expressivity as the AI-based element syntax used across the GS1 system, notably in the GS1 General Specifications. The GS1 Digital Link URI syntax distinguishes between primary keys, such as GTIN and GLN, key qualifiers, such as batch/lot and GLN extension, and attributes such as expiry date and ship-to address. The GS1 Digital Link URI syntax is the foundation on which all other aspects of the standard are built.
https://www.gs1.org/docs/Digital-Link/GS1_Digital_Link_Standard_URI_Syntax_r_i1-2-1_2022-02-08.pdf

This document provides some of the background to the design of GS1 Digital Link, highlighting existing techniques and practices that underpin the World Wide Web, and applying those to the GS1 system. The normative portions set out the detailed syntax of Web addresses (HTTP URIs) that encode GS1 identifiers with exactly the same precision and expressivity as the AI-based element syntax used across the GS1 system, notably in the GS1 General Specifications. The GS1 Digital Link URI syntax distinguishes between primary keys, such as GTIN and GLN, key qualifiers, such as batch/lot and GLN extension, and attributes such as expiry date and ship-to address. The GS1 Digital Link URI syntax is the foundation on which all other aspects of the standard are built.
GS1 Digital Link Standard
https://www.gs1.org/standards/gs1-digital-link
The GS1 Digital Link standard extends the power and flexibility of GS1 identifiers by making them part of the web. That means that GS1 identifiers, such as the GTIN, are now a gateway to consumer information that strengthens brand loyalty, improved supply chain traceability information, business partner APIs, patient safety information and more. Where a URL typically points to a single, specific website, GS1 Digital Link enables connections to all types of business-to-business and business-to-consumer information. If you’re adding a QR code or NFC tag to a product, using the GS1 standard means you’re not only providing a URL for people to scan, you’re also carrying GS1 identifiers – the same identifiers relied upon throughout industry – and following a non-proprietary, no vendor-lock system. This means the brand owner remains in complete control but can still link to any number of information sources, all from one symbol, saving space and improving efficiency.
https://www.gs1.org/standards/gs1-digital-link
The GS1 Digital Link standard extends the power and flexibility of GS1 identifiers by making them part of the web. That means that GS1 identifiers, such as the GTIN, are now a gateway to consumer information that strengthens brand loyalty, improved supply chain traceability information, business partner APIs, patient safety information and more. Where a URL typically points to a single, specific website, GS1 Digital Link enables connections to all types of business-to-business and business-to-consumer information. If you’re adding a QR code or NFC tag to a product, using the GS1 standard means you’re not only providing a URL for people to scan, you’re also carrying GS1 identifiers – the same identifiers relied upon throughout industry – and following a non-proprietary, no vendor-lock system. This means the brand owner remains in complete control but can still link to any number of information sources, all from one symbol, saving space and improving efficiency.
ISEAL Core Metadata on Sustainability
https://www.isealalliance.org/isealcoremetadata
This project sought to codify a shared language for the sustainability community. All certification schemes or sustainability initiatives are based on similar data concepts: certificate holders, certified sites, location coordinates, dates for audits, indicators for compliance, publications, normative frameworks, etc. When data and information are standardised, they can inform multiple purposes (e.g., using monitoring and evaluation data to inform compliance assessment, or combining multiple organisations’ compliance results to achieve a more comprehensive understanding of risk for a specific region), making them more valuable. This standardisation will enable standards to better align the ways they communicate and demonstrate their performance in the sustainability landscape—maximizing the data’s ability to generate cross-sector business insights and reach less-informed external audiences.
https://www.isealalliance.org/isealcoremetadata
This project sought to codify a shared language for the sustainability community. All certification schemes or sustainability initiatives are based on similar data concepts: certificate holders, certified sites, location coordinates, dates for audits, indicators for compliance, publications, normative frameworks, etc. When data and information are standardised, they can inform multiple purposes (e.g., using monitoring and evaluation data to inform compliance assessment, or combining multiple organisations’ compliance results to achieve a more comprehensive understanding of risk for a specific region), making them more valuable. This standardisation will enable standards to better align the ways they communicate and demonstrate their performance in the sustainability landscape—maximizing the data’s ability to generate cross-sector business insights and reach less-informed external audiences.
AIS, Automatic Identification System
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Automatic_identification_system
The automatic identification system (AIS) is an automatic tracking system that uses transceivers on ships and is used by vessel traffic services (VTS).
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Automatic_identification_system
The automatic identification system (AIS) is an automatic tracking system that uses transceivers on ships and is used by vessel traffic services (VTS).
EPCIS 2.0 Standard, full text
https://ref.gs1.org/standards/epcis/

EPCIS Standard enables disparate applications to create and share visibility event data, both within and across enterprises. Release 2.0, Ratified, Jun 2022.
https://ref.gs1.org/standards/epcis/

EPCIS Standard enables disparate applications to create and share visibility event data, both within and across enterprises. Release 2.0, Ratified, Jun 2022.
Maritime Mobile Service Identity (MMSI)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maritime_Mobile_Service_Identity
A Maritime Mobile Service Identity (MMSI) is effectively a maritime object's international maritime telephone number, a temporarily assigned UID, issued by that object's current flag state, (unlike an IMO, which is a global forever UID).
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maritime_Mobile_Service_Identity
A Maritime Mobile Service Identity (MMSI) is effectively a maritime object's international maritime telephone number, a temporarily assigned UID, issued by that object's current flag state, (unlike an IMO, which is a global forever UID).
Digital Container Shipping Association
https://dcsa.org/
At DCSA, we envisage a digitally interconnected container shipping industry in which customers have a choice of seamless, easy-to-use services that provide the flexibility to meet their business and sustainability goals.
https://dcsa.org/
At DCSA, we envisage a digitally interconnected container shipping industry in which customers have a choice of seamless, easy-to-use services that provide the flexibility to meet their business and sustainability goals.
Global Container Database
https://www.bic-boxtech.org/
Supply chain safety and efficiency through data visibility: A non-profit platform for container technical details
https://www.bic-boxtech.org/
Supply chain safety and efficiency through data visibility: A non-profit platform for container technical details
Global Location Number (GLN)
https://www.gs1.org/standards/id-keys/gln
Global Location Number (GLN) can be used by companies to identify their locations, giving them complete flexibility to identify any type or level of location required.
https://www.gs1.org/standards/id-keys/gln
Global Location Number (GLN) can be used by companies to identify their locations, giving them complete flexibility to identify any type or level of location required.
Global Trade Item Number (GTIN)
https://www.gs1.org/standards/id-keys/gtin
The Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) can be used by a company to uniquely identify all of its trade items. GS1 defines trade items as products or services that are priced, ordered or invoiced at any point in the supply chain.
https://www.gs1.org/standards/id-keys/gtin
The Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) can be used by a company to uniquely identify all of its trade items. GS1 defines trade items as products or services that are priced, ordered or invoiced at any point in the supply chain.
GS1 Traceability main page
https://www.gs1.org/standards/traceability
GS1-enabled traceability solutions provide the best path to interoperability, protect companies' investments and scale up. Greater levels of digitalisation, speed and data accuracy become possible. Each trading partner in the chain becomes free to choose the solution on the market that best meets its specific needs. GS1 provides the global and common language for traceability solutions and the ecosystem for its implementation. GS1 makes the industry vision operational and scalable through collaborations and community development, registries about products and places, capacity building and local implementation services in more than 100 countries.
https://www.gs1.org/standards/traceability
GS1-enabled traceability solutions provide the best path to interoperability, protect companies' investments and scale up. Greater levels of digitalisation, speed and data accuracy become possible. Each trading partner in the chain becomes free to choose the solution on the market that best meets its specific needs. GS1 provides the global and common language for traceability solutions and the ecosystem for its implementation. GS1 makes the industry vision operational and scalable through collaborations and community development, registries about products and places, capacity building and local implementation services in more than 100 countries.
EPCIS
https://www.gs1.org/standards/epcis
EPCIS is a GS1 standard that enables trading partners to share information about the physical movement and status of products as they travel throughout the supply chain – from business to business and ultimately to consumers. It helps answer the “what, where, when and why” questions to meet consumer and regulatory demands for accurate and detailed product information.
The goal of EPCIS is to enable disparate applications to create and share visibility event data, both within and across enterprises. This sharing is aimed at enabling users to gain a shared view of physical or digital objects within a relevant business context.
https://www.gs1.org/standards/epcis
EPCIS is a GS1 standard that enables trading partners to share information about the physical movement and status of products as they travel throughout the supply chain – from business to business and ultimately to consumers. It helps answer the “what, where, when and why” questions to meet consumer and regulatory demands for accurate and detailed product information.
The goal of EPCIS is to enable disparate applications to create and share visibility event data, both within and across enterprises. This sharing is aimed at enabling users to gain a shared view of physical or digital objects within a relevant business context.
Global Dialogue on Seafood Traceability (GDST)
https://traceability-dialogue.org
The GDST is an international, business-to-business platform established in 2017 to create the first-ever global industry standards for seafood traceability.
https://traceability-dialogue.org
The GDST is an international, business-to-business platform established in 2017 to create the first-ever global industry standards for seafood traceability.